With the increase in use of the bitcoin network, a lot of scalability issues are created. This is where the lightning network comes in.
The original Bitcoin network can handle only 7 transactions per second. This causes congestion and scalability issues due to its limited capacity, resulting in unreliable performance.
What is the lightning Network?
The lightning network is the off-chain approach to handle bitcoin transactions. It serves as an off-chain network designed for facilitating micro Bitcoin transactions, particularly smaller-value transactions. The purpose is to prevent congestion on the mainnet while simultaneously lowering excessive transaction fees.
How does the lightning network function.
We shall use the coffee shop analogy (example) to explain the working process of the lightning network:
Bob (a bitcoin holder) wants to buy coffee from a coffee shop (another bitcoin holder). They open a payment channel.

The payment channel is a multi-sig wallet (a wallet that can be accessed by two or more people).it will contain all the money going to be transacted during the lifespan of the payment channel.
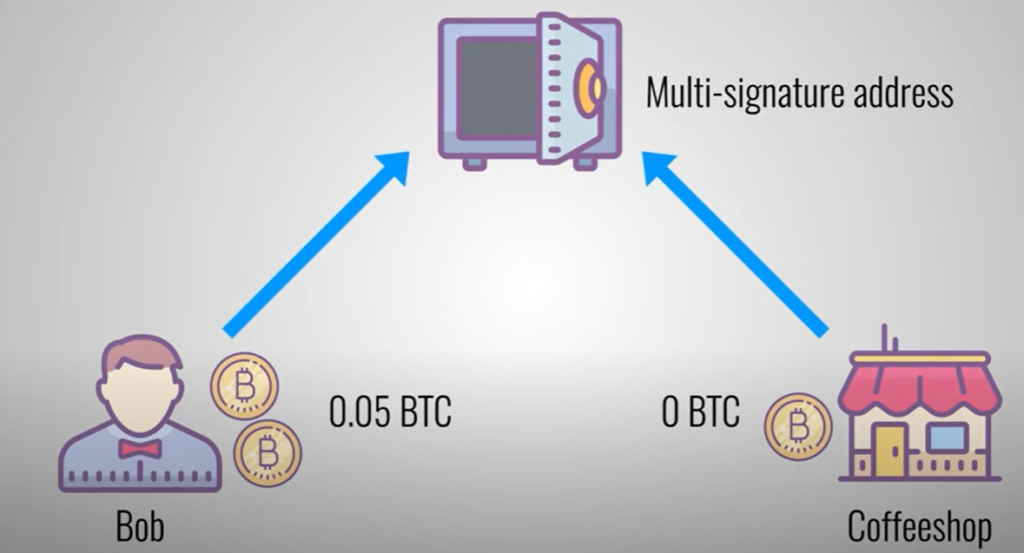
The multi-sig wallet will have a balance sheet that represents what balances “Bob” and the “coffee shop” have.

When a transaction is initiated, the balances adjust accordingly and is signed using the private keys of the parties involved to sign the balanced sheet.

Only the latest signed balance sheet is accepted to be closed to the bitcoin mainnet (to be executed on the bitcoin network).

To transfer from one person to another, the lightning network utilises already made payment channels from previous users to just transfer the payment without interrupting the bitcoin mainnet.
Conclusion.
Now that we have learnt the basics of what the lightning network is and how it works. Head over to Crypto University to get more insights on how to make the most from your lightning network experience.
